- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- Fiberglass and Insulation Sleeves
- Fire Resistant Sleeve
- Insulation Sleeves
- Polyester Expandable Braided Sleeves
- SRBP Tubes
- Polyurethane Fiberglass Sleeves 1.5 kv
- Acrylic Fiberglass Sleeving
- Varnished Fiberglass Sleeve F Class
- Fire Sleeves
- Polyurethane Fiberglass Sleeve
- PVC Coated Fiberglass Sleeve
- Silicone Coated Fiberglass Sleeve
- Polyurethane Coated Fiberglass Sleeves
- Fiberglass Sleeve ( China Sleeve )
- Fiberglass Sleeving B Class
- Nomex Paper and Electrical Insulation Papers
- Electrical Insulating Paper
- Eurotherm Laminated Nomex Paper NPN
- Pure Aramid Paper
- Laminated Fleece Paper
- Laminated Aramid Paper
- Saturated Fleece Paper
- DuPont Nomex Paper
- Saturated Fleece Paper
- Insulating Kraft Paper
- Insulation Pressboard
- Laminated Nomex
- Electrical Insulation Papers and Laminates
- Pure Aramid (Nomex) Paper
- Laminated Fleece
- Black Kraft Paper
- Amotforse Brown Kraft Paper
- Diamond dotted Paper
- Fiberglass and Insulated Cables
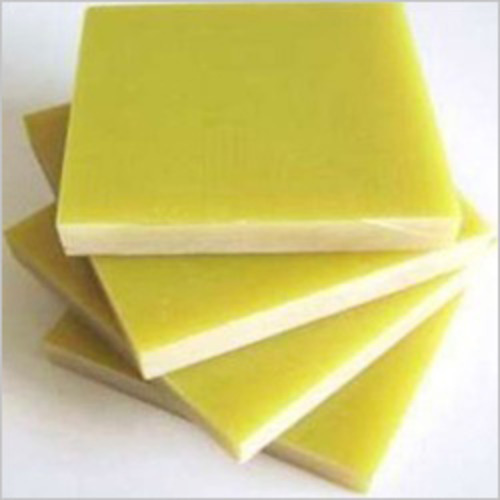
- Glass Epoxy Sheets and Wedges
- Varnishes and Thinners
- Electrical Insulation Tapes
- Electrical Insulation Sheets and Fabrics
- PTFE Wire
- Silicon Cable
- Insulation Film
- Fiberglass and Insulation Sleeves
- Certificates
- Contact Us
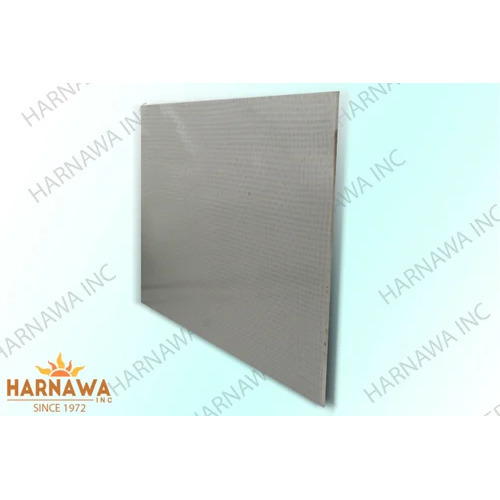
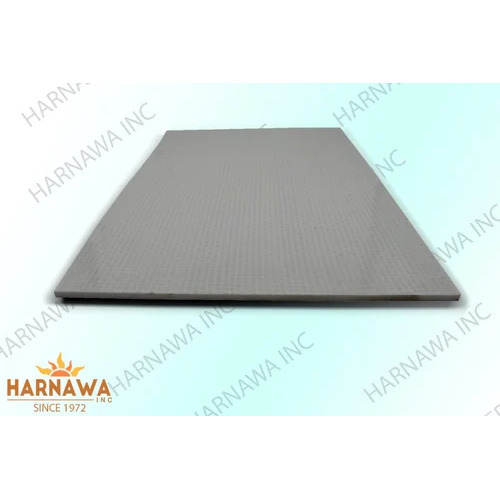
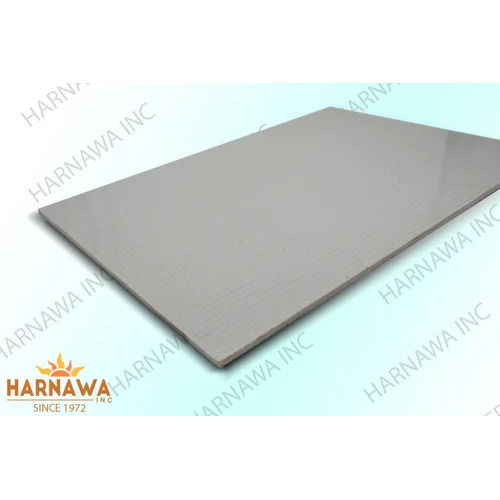
SMC FRP Sheets
250.0 INR/Kilograms
Product Details:
- Product Type Smc Sheets
- Material SMC
- Warranty Yes
- Color Black
- Display Type Nil
- Features Good Quality
- Click to view more
X
SMC FRP Sheet Price and Quantity
- 1 Piece
- 250.0 INR/Kilograms
SMC FRP Sheet Specification
- Good Quality
- Yes
- Smc Sheets
- SMC
- Nil
- Black
SMC FRP Sheet Trade Information
- 1000 Piece Per Month
- 7 Days
- North America, Central America, Africa, South America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, Asia, Australia, Middle East
- All India
Product Description
FRP (Fiber-Reinforced Plastic) and SMC (Sheet Moulding Compound) sheets are both materials utilised in many industries for diverse applications.
Here is a description of each:
SMC Sheets (Sheet Moulding Compound):
- SMC sheets are composite materials created by mixing several reinforcing components, such as glass fibres, with thermosetting resins (usually polyester or epoxy).
- The resulting SMC material has outstanding mechanical qualities and is rigid, light, and strong.
- SMC sheets are frequently used in the automotive industry to create a variety of parts, including bumpers, hoods, and body panels.
- Due to their insulating qualities, they are also utilised in the electrical and electronics industries for the creation of enclosures and coverings.
- SMC sheets are adaptable for a variety of applications since they may be compressed into intricate shapes.
Fiber-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Sheets:
- As the name implies, FRP sheets are plastic sheets reinforced with fibres, most frequently carbon or glass fibres.
- These sheets are renowned for their long lifespan, high strength-to-weight ratio, and resistance to corrosion.
- FRP sheets are frequently used in construction, especially when high strength and corrosion resistance are required, as in the manufacture of tanks, pipes, and structural elements.
- Due to their resistance to corrosion from water and salt, they are also utilised in the maritime industry for boat hulls and decks.
- Depending on the particular needs of the application, FRP sheets can also be reinforced with materials other than glass and carbon fibres.
SMC and FRP sheets both have benefits in terms of their material composition, such as resistance to corrosion, high strength, and adaptability in shaping.The project or applications particular requirements, as well as elements like cost, required design elements, and environmental considerations, will determine which of the two is best.
Sheets made of SMC (Sheet Moulding Compound) and FRP (Fiber-Reinforced Plastic) are both suited for a variety of applications due to their features and advantages.
The following are some of the main qualities and advantages of each material:
Sheet Moulding Compound (SMC) Sheets:
1. High Strength: SMC sheets are ideal for load-bearing applications due to their superior mechanical qualities, which include high tensile and flexural strength.
2. Lightweight: Compared to metals, SMC is comparatively light, which can result in weight reductions in applications like automotive components.
3. SMC is a favoured option for applications requiring corrosion resistance in outdoor and harsh climate settings because it is naturally resistant to corrosion.
4. Dimensional Stability: SMC sheets experience few dimensional changes as a result of temperature variations, ensuring long-term stability under a variety of circumstances.
5. Design Flexibility: SMC may be moulded into intricate, complex shapes, providing a variety of design alternatives.
6. SMC is a good material for electrical and electronic enclosures because of its outstanding electrical insulating qualities.
7. Low Maintenance: SMC components typically require little maintenance throughout the course of their lives because to their durability and corrosion resistance.
8. Fire Resistance: A few SMC formulations have strong fire resistance characteristics, which can be crucial in some applications.
Fiber-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Sheets:
1. FRP sheets are renowned for their outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, which provides tremendous strength while being lightweight.
2. FRP is highly corrosion-resistant, making it the best choice for applications where exposure to chemicals or moisture is a concern.
3. Durability: FRP sheets are strong and resistant against extreme weather, including UV exposure.
4. Customizability: To suit certain performance requirements, FRP can be customised by utilising different types of reinforcing fibres (such as glass, carbon, and aramid) and resin matrices.
5. FRP, like SMC, has high electrical insulating qualities, making it appropriate for use in electrical and electronic applications.
6. Thermal Insulation: Some FRP formulations have the ability to provide thermal insulation, which can be useful in some applications.
7. Low Maintenance: FRP components often only need minor upkeep, which lowers total lifecycle costs.
8. Design Flexibility: FRP may be formed into a variety of forms and sizes, enabling complicated geometries and elaborate designs.
9. Installation is reasonably simple with FRP sheets, which can cut down on time and labour expenses in building and other projects.
In conclusion, SMC and FRP sheets both combine strength, toughness, corrosion resistance, and design adaptability. The exact needs of the application, taking into account elements like load-bearing capability, environmental circumstances, and financial constraints, will determine which option is best.
FAQs ofSMC Sheets / FRP Sheets:
1. How do SMC and FRP sheets differ from one another?
Ans - In order to create SMC sheets, thermosetting resins are combined with reinforcements like glass fibres. FRP sheets, on the other hand, are plastic sheets that have been strengthened with fibres, most often carbon or glass. The fundamental distinction is in the composition, with FRP being a plastic sheet reinforced with fibres whereas SMC is a mixture of resin and fibres.
2. What are the main uses of SMC and FRP sheets?
Ans - In the automotive sector, SMC sheets are frequently used to create body panels, enclosures, and other parts. FRP sheets are used for tanks, boat hulls, and other structural components where corrosion resistance and high strength are requirements in the construction, marine, and chemical sectors.
3. Are SMC and FRP sheets made of eco-friendly materials?
Ans - Since corrosion resistance can lengthen product lifespans and lessen the need for frequent replacements, SMC and FRP sheets both have environmental advantages. However, the manufacturing procedure and disposal techniques also have an impact on the environment, thus it is important to take these into account.
4. Are SMC and FRP sheets recyclable?
Ans - Due to the thermosetting properties of the resins, SMC sheets are often harder to recycle. FRP sheets, particularly those made of thermoplastic matrices, may be more recyclable. It is advisable to contact manufacturers or recycling facilities for the most recent information because the recycling alternatives for these products are constantly changing.
5. What elements should I take into account while deciding between SMC and FRP sheets for my project?
Ans - Consider aspects including the individual application, load-bearing specifications, environmental conditions, budget, and design freedom when choosing between SMC and FRP sheets. While FRP excels in areas needing great strength and corrosion resistance, SMC might be more suited for complicated geometries and electrical applications.
Superior Quality and Performance
Our SMC FRP Sheets stand out for their robust build, resistance to corrosion, and impressive load-bearing capability. Thanks to their advanced surface treatment and precise manufacturing, these sheets maintain their appearance and functionality even in demanding industrial environments.
Versatile Industrial Application
Designed for wide-ranging industrial usage, these sheets provide dependable solutions for machinery covers, electrical insulation, panels, and more. Their flexible compatibility and adherence to stringent quality standards make them suitable for various sectors needing reliable and cost-effective materials.
FAQs of SMC FRP Sheets:
Q: How are SMC FRP Sheets manufactured for industrial use?
A: SMC FRP Sheets are produced by combining Sheet Moulding Compound with Fiber Reinforced Plastic, then curing the blend under heat and pressure. This results in robust, lightweight panels with consistent thickness and strength tailored for industrial requirements.Q: What are the advantages of using SMC FRP Sheets in industrial settings?
A: These sheets offer durability, chemical resistance, and insulation properties, making them ideal for industrial applications. Their color-coated surfaces resist fading and corrosion, ensuring long service life and minimal maintenance.Q: Where can SMC FRP Sheets be applied?
A: SMC FRP Sheets are commonly used in electrical insulation, machinery covers, wall panels, roofing, and other industrial projects requiring sturdy, non-conductive, and weather-resistant materials.Q: When should SMC FRP Sheets be chosen over traditional materials?
A: Select SMC FRP Sheets when projects demand a combination of strength, lightweight properties, corrosion and weather resistance, especially where metal or wood may fail to meet longevity and maintenance expectations.Q: What is the warranty coverage for your SMC FRP Sheets?
A: All our SMC FRP Sheets come with a warranty, covering manufacturing defects and quality issues, assuring customers of their reliability and long-term performance.Q: How does the surface treatment benefit the products lifespan?
A: The advanced color-coated surface treatment not only enhances visual appeal but also provides resistance to environmental factors, ensuring that the sheets remain intact and functional over many years of use.Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email

 Send Email
Send Email 










 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese